Page 749 - Tungaloy Catalog
P. 749
TAC Milling Inserts
Guideline for Selection of Inserts for Milling
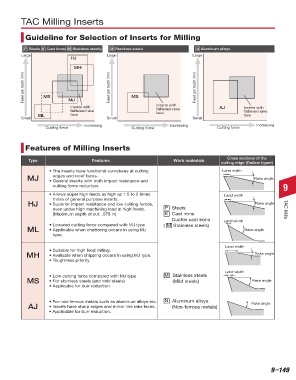
P Steels K Cast irons( M Stainless steels) M Stainless steels N Aluminum alloys
Large Large Large
HJ
MH
Feed per tooth limit MS Feed per tooth limit MS Feed per tooth limit
MJ
Inserts with Inserts with AJ Inserts with
flattened rake flattened rake flattened rake
ML face face face
Small Small Small
Increasing Increasing Increasing
Cutting force Cutting force Cutting force
Features of Milling Inserts
Cross sections of the
Type Features Work materials
cutting edge (Outline figure)
• The inserts have functional curvatures at cutting Land width
edges and relief faces.
MJ • General inserts with both impact resistance and Rake angle
cutting force reduction. 9
• Allows super high feeds as high as 1.5 to 2 times Land width
those of general purpose inserts.
HJ • Superior impact resistance and low cutting forces, Rake angle
even under high machining load at high feeds. P Steels TAC Mills
(Maximum depth of cut: .078 in) K Cast irons
Ductile cast irons Land width
• Lowered cutting force compared with MJ type ( M Stainless steels)
ML • Applicable when chattering occurs in using MJ Rake angle
type.
Land width
• Suitable for high feed milling.
MH • Available when chipping occurs in using MJ type. Rake angle
• Toughness priority.
Land width
• Low cutting force compared with MJ type M Stainless steels
MS • For stainless steels (and mild steels) (Mild steels) Rake angle
• Applicable for burr reduction.
• For non-ferrous metals such as aluminum alloys etc. N Aluminum alloys Rake angle
AJ • Inserts have sharp edges and mirror like rake faces. (Non-ferrous metals)
• Applicable for burr reduction.
Most unmarked items are available on a RFQ basis, contact your sales rep for more information.
9–149